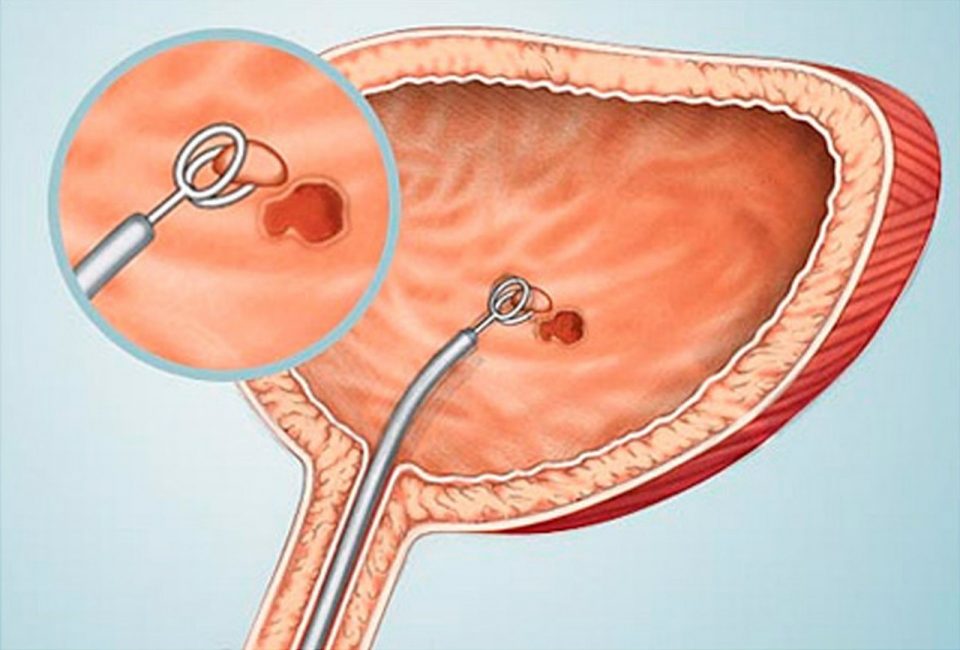
Cystoscopy is an examination of the inner surface of the bladder using a special optical device. A cystoscope with a microcamera is inserted through the urethra and allows the doctor to see with his own eyes what is happening inside.
Despite the fact that modern equipment allows this procedure to be carried out with minimal discomfort, patients often have questions: is it really necessary to perform this examination, is it possible to do without it, etc. In this article, I have collected several real-life images of the bladder mucosa obtained during cystoscopy to demonstrate how different the problems identified can be and how cystoscopy can help determine the diagnosis and treatment.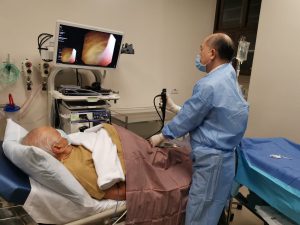
The indications for this procedure are determined by the doctor. Cystoscopy is performed:
with frequently recurring cystitis, despite adequate therapy and normal urine tests after treatment;
complaints of urination disorders with normal urine test values;
detection of an impurity of blood in urine: both visible to the eye (macrohematuria) and detected only by urine tests (microhematuria);
persistent long-term course of chronic cystitis despite adequate antibiotic therapy with a persisting elevated level of leukocytes in the urine (under the guise of antibiotics);
for control after surgery (after 3 months);
detection by ultrasound of the bladder of various types of formations and suspicion of oncology.
During cystoscopy, a biopsy of the bladder mucosa may be done. Biopsy is performed in all cases of proliferative cystitis, suspected metaplasia, interstitial cystitis. Thanks to a biopsy, you can accurately examine the structure and cellular composition of the altered tissue for an accurate diagnosis. Biopsies are taken only from the altered mucosa, their number is determined by the number of types of changes in the mucous membrane.
Depending on the picture seen, the doctor chooses an adequate treatment tactics. Some conditions that can be detected with cystoscopy:
1. Cystic cystitis. Cystoscopy allows you to accurately diagnose the problem due to visible changes. After the diagnosis is established, treatment is carried out with instillations with medicinal formulations.
2. Polypoid / bullous / papillary cystitis. Drug treatment, in some cases laser ablation of the bladder mucosa is more effective.
3. Inlaid cystitis. Cystoscopy allows you to see areas of altered mucosal tissue. The altered tissue is removed for treatment.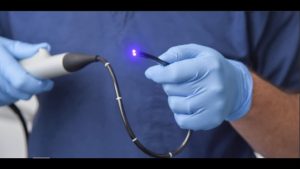
4. Metaplasia of the bladder mucosa. Laser ablation of the mucosa is performed.
5. Emphysematous cystitis. Quite a rare pathology, it is treated with medication, with the help of instillations.
Cystoscopy is a routine method for examining patients with various pathologies of the urinary system and is easily tolerated. On the Internet, you can find negative reviews about cystoscopy, but most often these reviews are associated with outdated equipment, or with insufficient anesthesia or non-compliance with the procedure technique.
For the least trauma to the mucous membranes of the urethra https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urethra and urinary bladder, a special gel with Lidocaine – Katejel is introduced before the procedure, this significantly reduces the pain during the procedure. Since the examination is carried out on modern equipment, with the use of an anesthetic, it takes place without pronounced painful sensations.
Normally, there may be an increase in urination, small cramps during urination, traces of blood in the urine, which disappear within 1-2 days.